Discussion
-
Questions from previous class
- Project Status
- Github Collection code repository
Collections
Learning objectives
- Know and use common methods in the Collections class
- Use the Iterator interface to traverse the elements in a collection
- Explore the relationship between interfaces and classes in Java
Java Arrays and Collections
Primitive Array - Core Java Type
Collection API - Lists, Sets, Queues
Generics and Typing Interfaces
Collection -Structure
LISTS
SETS
QUEUE
Collection Class
Collection Framework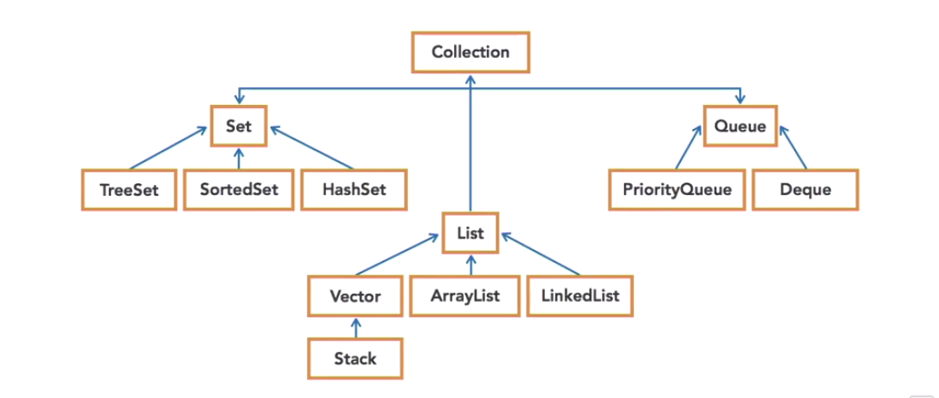
What is a Collection?
- A collection is a container object that holds a group of objects, often referred to as elements.
- A List is an ordered collection that allows duplicate elements.
- A Map stores key-value pairs, similar to a database table.
- A Set or Map can be either sorted or unsorted.
- Sorted collections guarantee iteration in a defined order, such as natural ordering or a comparator-defined order.
- Unsorted collections do not provide any guarantee about iteration order.
- Collections are dynamic and growable in nature.
Collection Framework
Collection Framework (Interface/Classes)
Interface
Implementations i.e . Classes
Algorithms
Java Arrays vs. Collections
| Array | Collection |
|---|---|
| Fixed size | Dynamic and resizable |
| Holds only homogeneous data | Can hold both homogeneous and heterogeneous data |
| Less memory-efficient compared to collections | More memory-efficient due to dynamic allocation |
| No built-in data structures | Uses built-in data structures and algorithms |
| Can store both primitive and object types | Stores only object types |
Collection vs. Collections
| Collection | Collections |
|---|---|
| Root interface of Java Collection Framework | Utility class for collection operations |
| Implemented by List, Set, and Queue | Provides utility methods like sort(), reverse(), shuffle(), etc. |
What is a Data Structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data efficiently. It not only holds data but also provides operations for accessing, modifying, and managing it.
What is a Container?
A container is a class that holds and organizes objects, such as arrays and lists. Containers define both an organizing structure and an interface for interacting with the stored elements.
Array
ArrayList
- Implements the
Listinterface. - Creates an object array that dynamically grows as needed. It can hold null values.
- Allows duplicate elements.
- Developers can add or remove elements using index values.
- The initial capacity can be set when the
ArrayListis created. ArrayListis a concrete class with a default initial capacity of ten.ArrayListis faster for retrieving data but slower for modifications.
ArrayList Examples
List
- The list interface is an ordered collection. Stores and access data in a sequential manner
- It extends the Collection interface
- List can include duplicate elements while sets cannot
- Github code sample List
Linked List
- LinkedList class can contain duplicate elements.
- It also implements the Queue interface
- LinkedList class can be used as list, stack or queue.
- Github code sample Linked List
Linked List
- Every nodes stores the data itself and a reference to next node
- It needs more memory than arrays
- It is a good choice for adding or removing elements from the list. It is slightly faster in a linked list.
- There is no need for shifting items.
- O(N) linear running time complexity
- A linked list uses a data structure called a doubly linked list
- A linked list is faster for manipulating data but slower for retrieval.
head node
next node
null
LinkedList VS ArrayList performance comparison
- Github code Comparison
Vector
- Vector use a simple one dimensional array.
- Java keeps doubling the size of the one dimensional array.
- Allows duplicate elements. Insertion order is preserved.
- Github code Vector
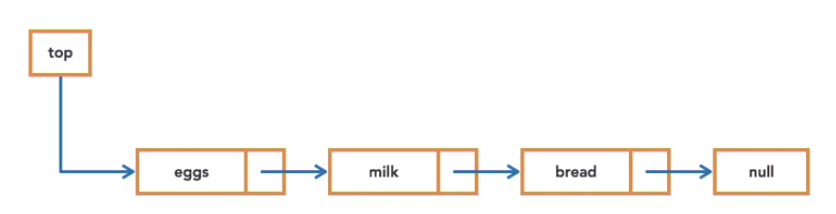
Stacks
- Similar to deck of cards,stack of plates
- A stack uses a last in, first out order (LIFO)
- Last item we inserted is the first item we take out
- It is an abstract data type
- pop(),push() and peek() are some methods
- Modern programming language are stack-oriented
Stacks
- Github code Stacks

Queues
- Similar to waiting in line
- It is abstract data type
- It is ordered collection
- A queue or FIFO (first in, first out)
- Basic operations enqueue(),dequeue() and peek()
- peek- get the item at the front of the queue, but don't remove it.
- used in operating systems and thread management(multithreading).Thread are stored in queues
Queues
- Github code Queues

PriorityQueue
- PriorityQueue class implements a priority queue
- Orders its elements according to their natural ordering using Comparable
- The element with the least value is assigned the highest priority and thus removed from the queue first.
- If there are several elements with the same highest priority the tie is broken randomly.
- peek() retrieves, but does not remove
- pool() retrieves and remove the heaod of this queue or returns null if this queue is empty
- Github code PriorityQueue
Deque
- It is pronounce as deck
- A deque is a double-ended queue that allows insertion and removal at either front or end
- Offer FIFO or LIFO behavior.
- Github code Deque