Learning objectives
- Understand the concept of recursion
- Understand differences between recursive and iterative code
- Be able to analyze and track execution flow of recursive code
What is Recursive?
- Recursive Function:– a function that calls itself directly or indirectly
- Each recursive call is made with a new, independent set of arguments
- Previous calls are suspended
- With each recursive invocation, the problem gets smaller and smaller until it cannot be made any more smaller.
- Is should have base case, otherwise it will be an infinite process
- Recursion process can be solved using loop.
- Recursion can be over kill for simpler solution.
Why we need Recursive?
- Break down big problems into smaller one.
- If you can divide the problem into smaller sub problem
- The problem statement is the same write the code to list the n...
- Recursion in data structure like trees and graphs
- Divide and conquer rule
- Commonly asked in the interview question
public class LogicBehindRecursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The stack memory works by LIFO last in first out
firstMethod();
}
static void firstMethod() {
secondMethod();
System.out.println("I am the first method");
}
static void secondMethod() {
thirdMethod();
System.out.println("I am the second method");
}
static void thirdMethod() {
fourthMethod();
System.out.println("I am the fourth method");
}
static void fourthMethod() {
System.out.println("I am the first method");
}
}
When to Avoid Recursive?
- If time and space complexity matters for us
- Recursion uses more memory
- Recursion can be slow due to adding to the stack
3 steps Recursive
- Recursive case– determine the size factor n!=n*(n-1)*(n-2)*......
- Base Case– the stopping condition 0!=1 1!=1
- Unintentional case- the constraint - factorial(-1)??
Recursion Examples
- Recursion behaves in the same way as if the function called another function.
- Infinite recursion occurs when there is no base case that serves as a terminating condition.
- In recursive program, infinite recursion will often result in an error that indicates that available memory has been exhausted.
- Github code sample Recursion
Infinite recursion
- Infinite recursion is just recursion without a terminating condition.
- Github code sample infinite recursion
Recursion vs. iteration
- Iteration can be used in place of recursion
- An iterative algorithm uses a looping construct
- A recursive algorithm uses a branching structure
- Recursive solutions are often less efficient, in terms of both time and space, than iterative solutions
- Recursion can simplify the solution of a problem, often resulting in shorter, more easily understood source code
Types of Recursion
- Direct a function calls itself
- Indirect function A calls function B, and function B calls function A =>
- function A calls function B, which calls …, which calls function A
Recursive Functions
- Recursive functions are used to reduce a complex problem to a simpler-to-solve problem.
- The simpler-to-solve problem is known as the base case
- Recursive calls stop when the base case is reached
- Github code sample Base case
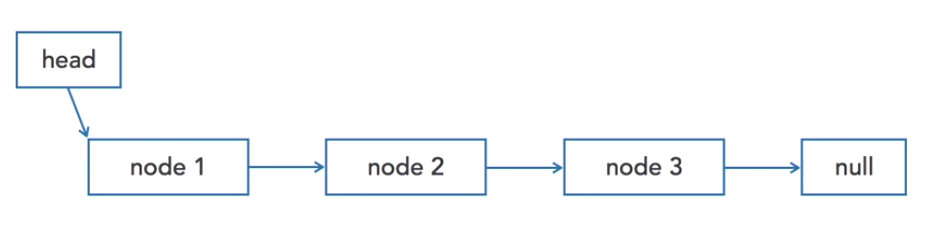
Linked List using Recursion
- Linked list follows to a recursive function
- Null reference as the base
- The next instance refers to any linked list that is not
empty which is a recursive call
- Github code sample Recursion Linked List
Thank you
Group Project Status