Discussion
-
Questions from previous class
- MidTerm I ( )
- Project Requirements/Team Update
- Github Code repository
- Github Project Management
- Group
Abstract classes & Interfaces
Abstract Class
- An abstract class is a placeholder in a class hierarchy that represents a generic concept .
- Abstract method exposes behavior that a child class must override
- We use the modifier abstract on the class header to declare a class as abstract:
- An abstract method is a method that is declared without an implementation (without braces, and followed by a semicolon)
- It can have abstract and non-abstract methods.
- Abstraction is a process of hiding the implementation details
Github code sample Abstract
public abstract class Vehicle{ //abstract class
public void drive() {
System.out.println("This is a drive method from Vehicle class");
}
public abstract String drive(String engineType); //abstract method
}
Why can't we create the object of an abstract class?
- Abstract class is incomplete
- It is the process of showing essential details and hiding the implementation
- There would be no actual implementation of the method to invoke
public class AbstractClass {
public void main(String[] args) {
Student IS247=new Student();
}
public abstract class Student{
}
}
Understanding Abstract Class
- Imagine you are designing a program for different animals.
- All animals make a sound, but the exact sound depends on the animal.
Challenge
- Modify the previous code to add more animals.
- Create a Cat class that extends the Animal class and implements the makeSound() method to print "Meow! Meow!"..
// Cat class implementing makeSound()
class Cat extends Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow! Meow!");
}
}
Interface
- Interface allows Abstraction, Only abstract methods are allowed
- On implementation of an interface, you must override all of its methods
- A class can implements multiple interfaces
- Interface defines the body to the method
- Like abstract classes, interfaces cannot be used to create objects
- A class can implement multiple interfaces, unlike inheritance (which allows only one superclass).
interface Revenue{} //Interface Revenue
class Marketing implements Revenue{} //Marketing class is
// a concrete class that implements Revenue interface
Demo Interface
Demo Abstract Class and Interface
Github code sample Abstract/Interface
challenge
- Implement the makeSound() method to print "Meow! Meow!"
- In the Main class, create both Dog and Cat objects and call their makeSound() method.
class Cat implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow! Meow!");
}
}
Example Abstract
Github code sample Abstract
Demo Interface
Github code sample Interface
Abstract VS Interface
source:media.geeksforgeeks.org
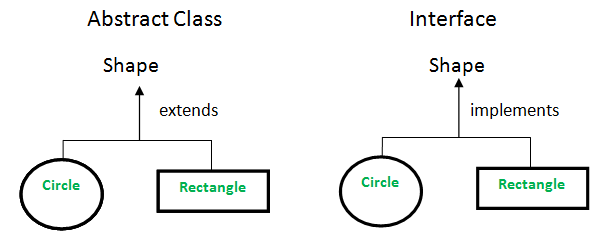
abstract class Shape{}
class Circle extends Shape{}
interface Shape{}
class Circle implements Shape{}
Abstract Classes VS Interfaces
| Feature | Abstract Class | Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A class that can have both abstract and concrete methods. | A blueprint that only contains abstract methods (until Java 8, which introduced default methods). |
| Method Implementation | Can have both abstract and fully implemented methods. | Only abstract methods (default and static methods were added in Java 8). |
| Variables | Can have instance variables (fields) with any access modifier. | Only public, static, and final variables are allowed. |
| Access Modifiers | Methods can be public, protected, or private. | Methods are public by default. |
| Multiple Inheritance | A class can extend only one abstract class. | A class can implement multiple interfaces. |
| Constructors | Can have constructors. | Cannot have constructors. |
| Use Case | Used when classes share behavior but also need customization. | Used for defining contracts that multiple unrelated classes must follow. |
Abstraction
- Way to arrange the code
- Suppresses details
- Interface over Abstract Classes
- Both abstract class and interface helps in polymorphism
Consider Using Abstract Class
- You want to share code among several closely related classes(Person -name,dob,gender...)
- You expect that classes that extend your abstract class have many common methods or fields, or require access modifiers other than public (such as protected and private).
- Use an abstract class when a template needs to be defined for a group of subclasses
- Abstract class helps in data encapsulation
Consider Using Interface
- You want to specify the behavior of a particular data type, but not concerned about who implements its behavior
- Use an interface when a role needs to be defined for other classes, regardless of the inheritance tree of these classes
- You want to take advantage of multiple inheritance of type
Demo Abstract Class
Github code sample Abstract
Built in Interface
- Interface Comparable
- This interface imposes a total ordering on the objects of each class that implements it. This ordering is referred to as the class's natural ordering, and the class's compareTo method is referred to as its natural comparison method
- Any class can implement Comparable to provide a mechanism for comparing objects of that type
- Java docs Comparable Interface
- Github code CompareableBuiltInInterface.java
Open-Closed Principle (OCP)
- Open for Extension, Closed for Modification Principle
- Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification
- Open for Extension =Extend existing behavior(Can derive from base class and override methods)
- Closed for Modification = Existing code remains unchanged(Avoid modifying Base class)
- Allow clients to access the original class with abstract interface
- Github code sample OCP
OCP Problem Challenge
- What’s Wrong?
- Every time a new medium (e.g., WhatsApp, Twitter, Instagram) is added, we need to modify the sendOTP method.
- This violates OCP because we are modifying the existing class instead of extending it.
OCP Solution
- Challenge
- Extend the functionality: Create a new class for SMSNotification.
Liskov Substitution Principle(LSP) Problem
- Derived classes must be completely substitutable for their base classes
- A subclass should be able to substitute its superclass without breaking functionality.
- if class A is a subtype of class B, we should be able to replace B(sub class) with A(super class) without disrupting the behavior of our program
- Github code sample LSP
- What’s Wrong?
- The Penguin class overrides fly() but throws an exception because penguins cannot fly.
- This means the subclass does not behave like its superclass, breaking the principle..
Liskov Substitution Principle(LSP) Solution
- Challenge
- 🛠️ Your Task: 1️⃣ Create a new class Ostrich that follows LSP correctly. 2️⃣ Ensure Ostrich does not implement fly() since it can't fly. 3️⃣ Test your solution by creating an Ostrich object and calling its eat() method.
Liskov Substitution Principle(LSP) Full Solution
Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- A class should not be forced to implement interfaces it does not use.
- The interfaces should split into smaller one
- Do not force the client to use the methods that they do not want to use
- Github code sample ISP
- Cash Payments don’t need payByCard(), payByMobile(), or payByQR().
- Card Payments don’t need payCash().
- Some payment types may not offer Cashback.
- A class like "OnlinePayment" would be forced to implement payCash(), which makes no sense.
What is wrong?
Interface Segregation Principle Solution
- Challenge
- 🛠️ Your Task: Create a new interface for crypto payments. Implement a CryptoPayment class that follows ISP. Ensure that the CryptoPayment class is not forced to implement unnecessary methods like payCash() or payByCard(). Modify the main method to test crypto payments along with other payment methods.
Interface Segregation Principle Challenge Solution