Discussion
- How to Zip HW/Labs?
- Project Requirements and groups
- Github Account
- Github Code repository
- Github project management
- Git installation
- Github Markdown
Exceptions Handling
Github Code repository
Exception Cases
@startuml
actor User
User--> (file) #line:red;line.bold;text:red : File not found
User--> (database) #line:red;line.bold;text:red : Database unreachable
User--> (application) #line:red;line.bold;text:red : Application error
User--> (network) #line:red;line.bold;text:red : Network error
@enduml
Exception
Unanticipated events that interrupt the flow of the execution in a program. It would terminate the program abnormally.
Exception Handling
Providing an alternative way
Providing friendly message to end user
Enough information to Debug the problem
Exception
- Compile Time Errors
- Logical Errors
- Runtime Errors
Compile Time Errors
- Cannot find symbol
- Incompatible Types
- Invalid Method Declaration
public static void main(String main[]){
System.out.println(j);
}
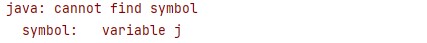
Logical Errors
Commonly made by developers
//The output is -336
public static void main(String main[]){
int i=1000;
byte b=(byte)i;
System.out.println(b*14);
}
Runtime Errors
- Termination of program
- Unfriendly error message
- Improper shutdown of the resources
public class ShowRuntimeErrors {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1 / 0);
}
}

What happens during exception?
- Name of the exception
- Description
- Location stacktrace
- JVM checks who is handling the exception
- Github code
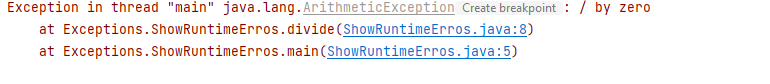
Demo
Method Exception
- LAB => What will happen in line 6,10,14?
- Github code
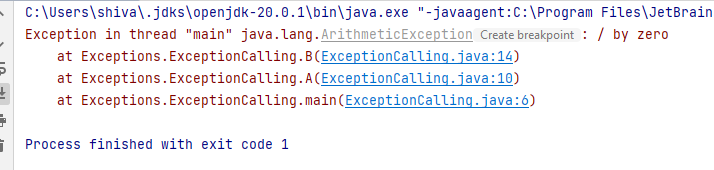
NumberFormatException Challenge
ArithmeticException
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1 / 0);
}
}
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(LAB)
- LAB =>Is the third print statement reachable?
- Github code
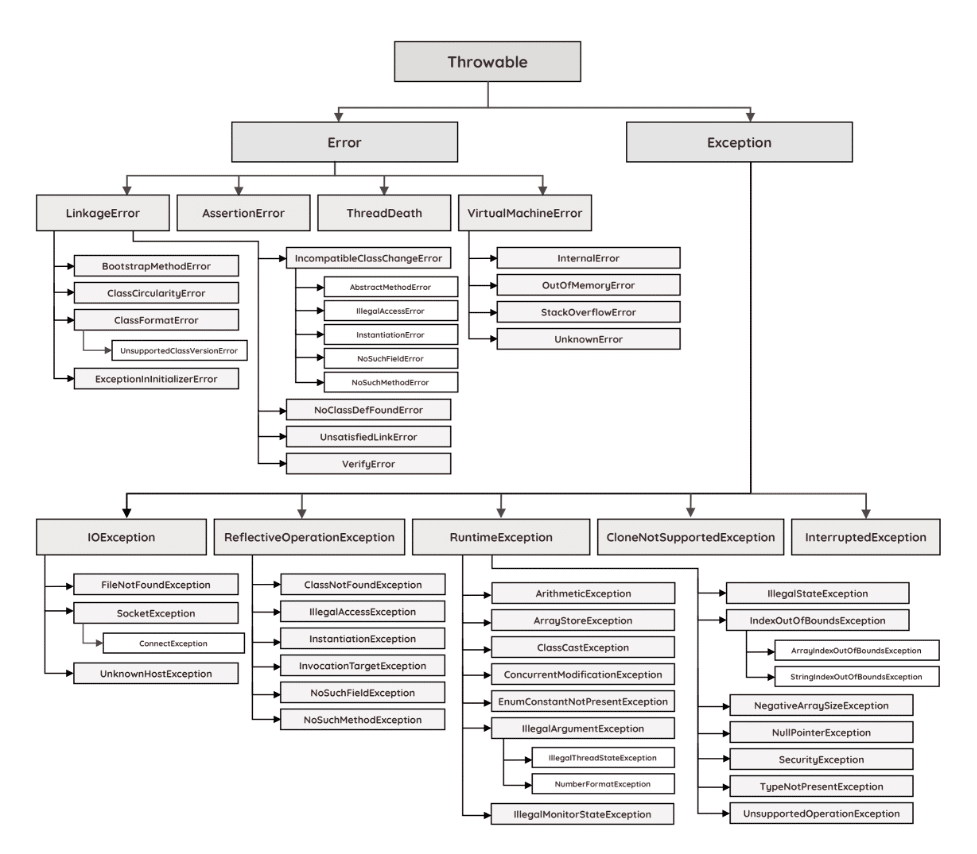
Exception Hierarchy
- Source:https://cdn.rollbar.com
- Check Error and Exception class
Why Exceptions?
- It is a way to signal errors on the application.
- Special object that indicates an error.
- Try/catch/finally are the keywords for handling exceptions
- Try=> normal code execution where everything is expected to go well.
- Catch=> if there is an error catch is called.
- Finally=> This is a cleanup code. This will run in any cases
- Exceptions are propagate to the call stack
- Exceptions object belongs throwable object hierarchy
- Exceptions can end your application
- Exception is a class
Try/Catch
try {
// code that may throw an exception
} catch (Exception e) {
// code to handle the exception
}
try {
System.out.println(1 / 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("End of the program");
Try catch finally syntax
Challenge
Exception Constructor
- Exceptions are objects like everything in java.
- It has constructors, methods just like other objects.
- Exception is a class
- Exception()/Exception(message)/Exception(cause)/Exception(message,cause) Github Github code
Exception Handling
- Try (Wrap any code that could cause error)
- Catch ( block, print an error message)
- Finally ( block is executed regardless of whether an exception occurred or not)
- Throw (Error with custom message)
- Exception Handling code
Lab No Matching Exceptions Challenge
- NotMatchingException code
- Lab=> How do we correct this code?
Checked/Unchecked Exceptions
- Checked exceptions Compiler raises an error if not handled
- Checked exception must be caught on try catch block or should be declared to throws
- Checked at the compile-time when the code is compiled
- Unchecked exceptions Compiler does not enforce handling. eg. RuntimeException
- Unchecked exceptions are the exceptions that are checked at run time
- Unchecked exceptions extend the RuntimeException.Checked Exceptions are all the rest
- Both checked and unchecked exceptions will crash your app if not handled
- Sample code on Github CheckedException
Lab Multiple Catch
Multiple Catch
Declaring, Throwing, and Catching Exceptions
LAB File I/O exception
Github code File IO
Throw Keyword
When exception is thrown it must of subclass
throw throwableInstance;
ArithmeticException e = new ArithmeticException("you can't divide by zero");
throw e;
throw new ArithmeticException("you can't divide by zero");
Throw can be used
To throw a new instance of a built-in exception
Used inside a method or block of code to explicitly throw an exception.
Inside custom exception
Rules for throw
- Exception object must be initialized
- No statments are allowed after throw statement.
- only Throwable types can be thrown
ArithmeticException e=null ;
throw e;
ArithmeticException e = new ArithmeticException("you can't divide by zero");
throw e;
System.out.println("Why i am getting error");
throw new Test();
class Test{}
class Test extends RuntimeException{}
throw new Test();
Throws
Github code File IO
Common Java Exceptions
String str= null;
int length = str.length(); //throws NullPointerException(Unchecked ex)
int[] arr = new int[5];
int x=array[9]; //throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(Unchecked ex)
int x=Integer.parseInt("abc"); //throws NumberFormatException(Unchecked ex)
Filereader fr = new FileReader("file.txt"); //throws FileNotFoundException(Checked ex)
Try With Resources
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("file.txt");
// Code that uses the reader
} catch (IOException e) {
// Exception handling
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Exception handling for close() method
}
}
}
try (FileReader reader1 = new FileReader("file.txt")) {
// Code that uses the resource
} catch (IOException e) {
// Exception handling
}
// The resource is automatically closed here
}
Try With Multiple Resources
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileReader reader = new FileReader("input.txt");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("output.txt")
) {
// reader = new FileReader("x.txt");
int character;
while ((character = reader.read()) != -1) {
writer.write(character);
}
System.out.println("File copied successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while reading or writing the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Custom Exceptions
- Define custom exception classes if the predefined classes are not sufficient.
- Define custom exception classes by extending Exception or a subclass of Exception
- Use the exception classes in the API whenever possible
- Sample code on Github Custom Exceptions
Lab Custom Exception
Errors vs Exception
| Errors | Exceptions |
|---|---|
| The error indicates trouble that primarily occurs due to the scarcity of system resources. | The exceptions are the issues that can appear at runtime and compile time. |
| It is not possible to recover from an error. | It is possible to recover from an exception. |
| In java, all the errors are unchecked. | In java, the exceptions can be both checked and unchecked. |
| The system in which the program is running is responsible for errors. | The code of the program is accountable for exceptions. |
| They are described in the java.lang.Error package. | They are described in java.lang.Exception package |