Object-Oriented Thinking
Refactor
- Don’t put everything into one class.
- Follow Single Responsibility principles.
Refactor
- Code refactor: Modifying existing code for improvement without changing functionality.
- Goals: Enhancing code quality, readability, and efficiency.
- Benefits: Improved structure, reduced duplication, easier maintenance.
- Focus: Making code concise, modular, and performant.
- Result: Enhanced software performance and maintainability.
Which code is better?
Problem code
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String major;
// other attributes and methods...
public void processStudentData() {
// Step 1: Validate student data
if (name == null || name.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid name");
return;
}
if (age <= 0 || age > 100) {
System.out.println("Invalid age");
return;
}
if (major == null || major.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid major");
return;
}
// Step 2: Perform calculations
double averageGrade = calculateAverageGrade();
String gradeLevel = calculateGradeLevel();
// Step 3: Print student information
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Age: " + age);
System.out.println("Major: " + major);
System.out.println("Average Grade: " + averageGrade);
System.out.println("Grade Level: " + gradeLevel);
// ... more print statements
// Step 4: Perform additional actions
if (averageGrade >= 90) {
System.out.println("Congratulations on your excellent performance!");
} else {
System.out.println("Keep up the good work!");
}
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String major;
// other attributes and methods...
public void processStudentData() {
if (!validateStudentData()) {
return;
}
double averageGrade = calculateAverageGrade();
String gradeLevel = calculateGradeLevel();
printStudentInformation(averageGrade, gradeLevel);
performAdditionalActions(averageGrade);
}
private boolean validateStudentData() {
if (name == null || name.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid name");
return false;
}
if (age <= 0 || age > 100) {
System.out.println("Invalid age");
return false;
}
if (major == null || major.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid major");
return false;
}
return true;
}
private double calculateAverageGrade() {
// ... implementation
}
private String calculateGradeLevel() {
// ... implementation
}
private void printStudentInformation(double averageGrade, String gradeLevel) {
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Age: " + age);
System.out.println("Major: " + major);
System.out.println("Average Grade: " + averageGrade);
System.out.println("Grade Level: " + gradeLevel);
// ... more print statements
}
private void performAdditionalActions(double averageGrade) {
if (averageGrade >= 90) {
System.out.println("Congratulations on your excellent performance!");
} else {
System.out.println("Keep up the good work!");
}
// ... more conditional statements and actions
}
// other methods...
}
Class
- In object-oriented programming (OOP), a class is a blueprint or template for creating objects.
- It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that objects of that class can have
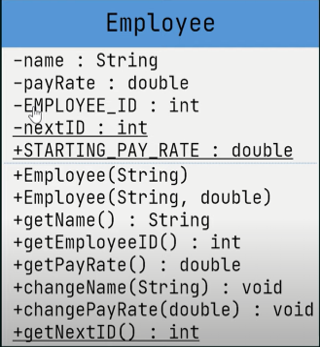
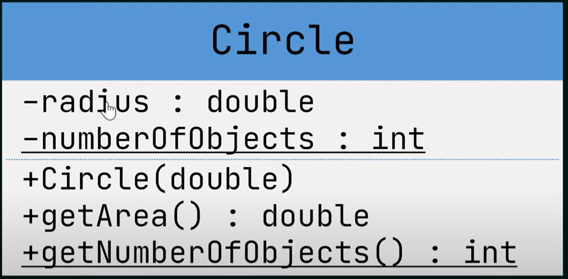
Example of class
public class Car {
// Attributes (properties)
private String make;
private String model;
private int year;
private double price;
// Constructor
public Car(String make, String model, int year, double price) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
this.price = price;
}
// Methods (behaviors)
public void start() {
System.out.println("The car is starting...");
}
public void accelerate() {
System.out.println("The car is accelerating...");
}
public void brake() {
System.out.println("The car is braking...");
}
// Getters and setters (accessor and mutator methods) for the attributes
public String getMake() {
return make;
}
public void setMake(String make) {
this.make = make;
}
// Other getter and setter methods for model, year, and price...
}
Sample code on Github class code
CLASSES
C1
C2
C3
C4
public class C1 {
}
public class C2 {
}
public class C3 {
}
public class C4 {
}
Incremental Build Code
Incremental Build Code
C1
C2
C3
C4
Object Integration
Objects are connected
C1
C2
C3
C4
Object
- Objects in Java are instances of classes..
- They represent specific entities or concepts within a program..
- Objects have their own state (attribute values What it knows (e.g., color, price, name).) and behavior (methods What it does (e.g., ring, drive, calculate).).
- Each object is created using a class as a blueprint.
- Objects can interact with each other by invoking methods and exchanging data.
- E.g. table, car etc. It can be tangible and intangible. The example of intangible object is banking system
public class CarObject {
String brand;
String color;
int year;
// Method
void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving the " + color + " " + brand + "!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of the Car class
CarObject myCar = new CarObject();
// Setting attribute values
myCar.brand = "Toyota";
myCar.color = "Red";
myCar.year = 2022;
// Accessing object's attributes and invoking method
System.out.println("My car is a " + myCar.year +
" " + myCar.brand + " in " + myCar.color + " color.");
myCar.drive();
}
}
public class Student {
int number = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student myStudent1 = new Student(); // Object 1
Student myStudent2 = new Student(); // Object 2
System.out.println(myStudent1.number);
System.out.println(myStudent2,number);
}
}
Sample code on Github object code
Principle of OOP
Abstraction
Polymorphism
Inheritance
Encapsulation
Also known as (APIE)
Class/object/Function/Method
APIE
Inheritance
- A class can extend another class.
- Inheritance implements the "IS A" relationship between objects
- A class can implements interface, methods members from its parent class.
- In Java, inheritance is denoted using the extends keyword.
- Inheritance is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming, facilitating code organization, reuse, and abstraction.
- Java Supports only public inheritance
- Employee is a parent/super class Fulltime and Partime is a sub/child class
class FullTimeEmployee extends Employee {
FulltimeEmployee() {
System.out.println("calling Constructor");
}
}
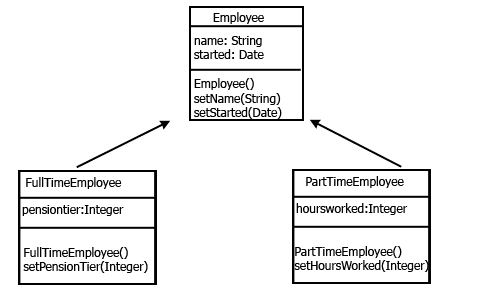
Inheritance Constructor Call
class A{
public A() {
System.out.println("New A");
}
}
class B extends A{public B(){
super();
System.out.println("New B");
}
}
Composition (Has-A)
- Something is made up of other parts
- Car contains wheel and engine
- It is also called aggregation
- In Java, inheritance is denoted using the extends keyword.
- Composition (HAS-A) simply mean use of instance variables that are references to other objects. For example: Car has Engine, or House has Bathroom
- Car has a Wheel, car has A Engine
- Github code samples composition
class Student {
int rollnumber;
String name;
Address address; //Composition
}
class Address{
String street;
String state;
}
Encapsulation
- Encapsulation is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit.
- As in encapsulation, the data in a class is hidden from other classes, so it is also known as data-hiding
- Encapsulation can be achieved by: Declaring all the variables in the class as private and writing public methods in the class to set and get the values of variables.
- Generally using access modifier you can achieve encapsulation.
- Github code samples Encapsulation
public class Student {
private String name; //private access modifier
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("Shiva Sharma");
System.out.println(s.getName());
}
Polymorphism
- The term polymorphism means "having many forms/shapes/Behavior"
- A polymorphism reference is a reference variable that can refer to different type of objects at different point in time. E.g. loop, method Obj.doIT();
- Polymorphism behave differently with different objects
- Types of polymorphism in java: Static, Dynamic, Runtime and Compile time Polymorphism.
- Method Overloading => compile time polymorphism.
- Method Overriding => Runtime polymorphism
- Static binding =>The binding which can be resolved at compile time by compiler is known as static or early binding.
- Github code samples Polymorphism
class Animal {
public void sound() {
System.out.println("The animal makes a sound.");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("The dog barks.");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("The cat meows.");
}
}
public class PolymorphismExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal1 = new Dog();
Animal animal2 = new Cat();
animal1.sound(); // Calls the sound() method of the Dog class
animal2.sound(); // Calls the sound() method of the Cat class
}
}
Abstraction
- It is a process of hiding the implementation detail and only showing essential information.
- Abstract classes cannot be instantiated but can be extended by subclasses.
- Abstraction can be achieved with either abstract classes or interfaces
- Github code samples Abstraction
abstract class Animal {
public abstract void animalSound();
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Zzz");
}
}
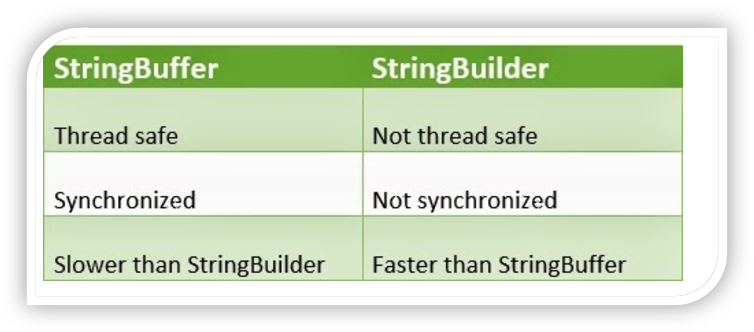
StringBuilder and StringBuffer Class
- StringBuilder and StringBuffer classes are used whenever a string is used.
- They are more flexible than string.
- They are mutable i.e. it can be changed
- You can add, insert or append new contents into these classes
- StringBuilder is more efficient if it is accessed by just a single task.
- StringBuilder class
- StringBufferclass
- Github code samples StringBuilder/Buffer
public static void main(String args[]) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer("test");
sBuffer.append(" String Buffer");
System.out.println(sBuffer);
StringBuilder sBuilder = new StringBuilder("test");
sBuilder.append(" String Builder");
System.out.println(sBuilder);
}
toString() Method
- The toString() method is a method defined in the Object class,
- It is the base class for all other classes.
- It is used to obtain a string representation of an object.
- Java override the toString() method to provide a more meaningful string representation of the object's state.
- The overridden toString() method can be customized based on the specific requirements of the class.
- Github code samples toString()
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}
public class ToStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("John Doe", 30);
System.out.println(person.toString()); // Output: Person{name='John Doe', age=30}
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}
public class ToStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("John Doe", 30);
System.out.println(person.toString()); // Output: Person{name='John Doe', age=30}
}
}