MultiDimensional Arrays
Chapter 8
Code Repo
Motivations
- Arrays of Arrays
- It is similar to table with rows and columns
- Thus far, you have used one-dimensional arrays to model linear collections of elements. You can use a two-dimensional array to represent a matrix or a table. For example, the following table that describes the distances between the cities can be represented using a two-dimensional array.

Motivations

Declare/Create Two-dimensional Arrays
// Declare array ref var
dataType[][] refVar;
// Create array and assign its reference to variable Memory allocation
refVar = new dataType[10][10];
// Combine declaration and creation in one statement
dataType[][] refVar = new dataType[10][10];
// Alternative syntax
dataType refVar[][] = new dataType[10][10];
Declaring Variables of Two-dimensional Arrays and Creating Two-dimensional Arrays
int[][] matrix = new int[10][10];
// or
int matrix[][] = new int[10][10];
matrix[0][0] = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++)
matrix[i][j] = (int)(Math.random() * 1000);
double[][] x;
Motivations

//a
matrix.length? 5
matrix[0].length? 5
//c
array.length? 4
array[0].length? 3
Declaring, Creating, and Initializing Using Shorthand Notations
- You can also use an array initializer to declare, create and initialize a two-dimensional array. For example
int[][] array = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9},
{10, 11, 12}
};
int[][] array = new int[4][3];
array[0][0] = 1; array[0][1] = 2; array[0][2] = 3;
array[1][0] = 4; array[1][1] = 5; array[1][2] = 6;
array[2][0] = 7; array[2][1] = 8; array[2][2] = 9;
array[3][0] = 10; array[3][1] = 11; array[3][2] = 12;
Lengths of Two-dimensional Arrays
int[][] x = new int[3][4];

MultiDimension Array Example
Code
- Array print days
Adding Values to a Two-dimensional Array
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] cars = {
{"Camaro","Corvette","Silverado"},
{"Mustang","Ranger","F-150"},
{"Ferrari","Lambo","Tesla"}
};
for(int i=0; i < cars.length; i++) {
System.out.println();
for(int j=0; j < cars[i].length ; j++) {
System.out.print(cars[i][j]+ " ");
}
}
}
}
Initializing arrays with input values
java.util.Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter " + matrix.length + " rows and " +
matrix[0].length + " columns: ");
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[row].length; column++) {
matrix[row][column] = input.nextInt();
}
}
Initializing arrays with random values
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[row].length; column++) {
matrix[row][column] = (int)(Math.random() * 100);
}
}
Printing arrays
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[row].length; column++) {
System.out.print(matrix[row][column] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
Printing arrays
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[row].length; column++) {
System.out.print(matrix[row][column] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
Summing all elements by column
Summing all elements
int total = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[row].length; column++) {
total += matrix[row][column];
}
}
Passing Tow-Dimensional Arrays to Methods
Problem: Grading Multiple-Choice Test
Problem: Finding Two Points Nearest to Each Other
Multidimensional Arrays
- Occasionally, you will need to represent n-dimensional data structures. In Java, you can create n-dimensional arrays for any integer n
- The way to declare two-dimensional array variables and create two-dimensional arrays can be generalized to declare n-dimensional array variables and create n-dimensional arrays for n >= 3.
Multidimensional Arrays
With student scores[i][j][k]
Student [i] exam[j] Multiple-Choice or essay[k]
double[][][] scores = {
{{7.5, 20.5}, {9.0, 22.5}, {15, 33.5}, {13, 21.5}, {15, 2.5}},
{{4.5, 21.5}, {9.0, 22.5}, {15, 34.5}, {12, 20.5}, {14, 9.5}},
{{6.5, 30.5}, {9.4, 10.5}, {11, 33.5}, {11, 23.5}, {10, 2.5}},
{{6.5, 23.5}, {9.4, 32.5}, {13, 34.5}, {11, 20.5}, {16, 7.5}},
{{8.5, 26.5}, {9.4, 52.5}, {13, 36.5}, {13, 24.5}, {16, 2.5}},
{{9.5, 20.5}, {9.4, 42.5}, {13, 31.5}, {12, 20.5}, {16, 6.5}}
};
Problem: Calculating Total Scores
Problem: Weather Information
Ragged Arrays
Each row in a two-dimensional array is itself an array. So, the rows can have different lengths. Such an array is known as a ragged array. For example,
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{2, 3, 4, 5},
{3, 4, 5},
{4, 5},
{5}
};
matrix.length is 5
matrix[0].length is 5
matrix[1].length is 4
matrix[2].length is 3
matrix[3].length is 2
matrix[4].length is 1
Ragged Array Example
Code
Ragged Arrays
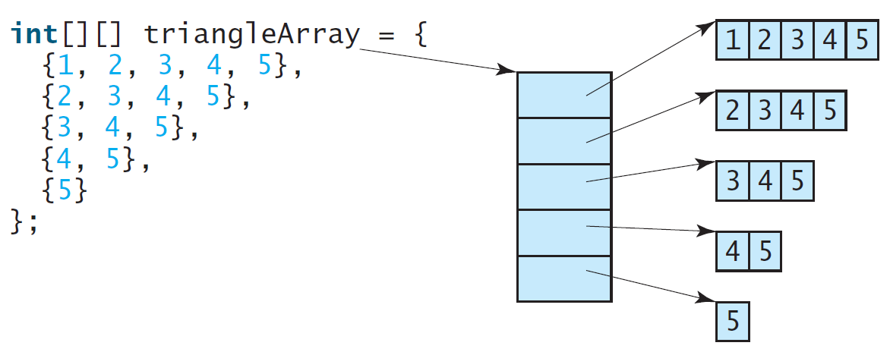
Ragged Arrays

int[][] x = new int[3][4];
