Methods
Chapter 6
Code Repo
Opening Problem
Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
sum += i;
System.out.println("Sum from 1 to 10 is " + sum);
sum = 0;
for (int i = 20; i <= 30; i++)
sum += i;
System.out.println("Sum from 20 to 30 is " + sum);
sum = 0;
for (int i = 35; i <= 45; i++)
sum += i;
System.out.println("Sum from 35 to 45 is " + sum);
Solution
public static int sum(int i1, int i2){
int sum=0;
for (int i = i1; i <= i2; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Sum from 1 to 10 is " + sum(1, 10));
System.out.println("Sum from 20 to 30 is " + sum(20, 30));
System.out.println("Sum from 35 to 45 is " + sum(35, 45));
}
Exercise
Code
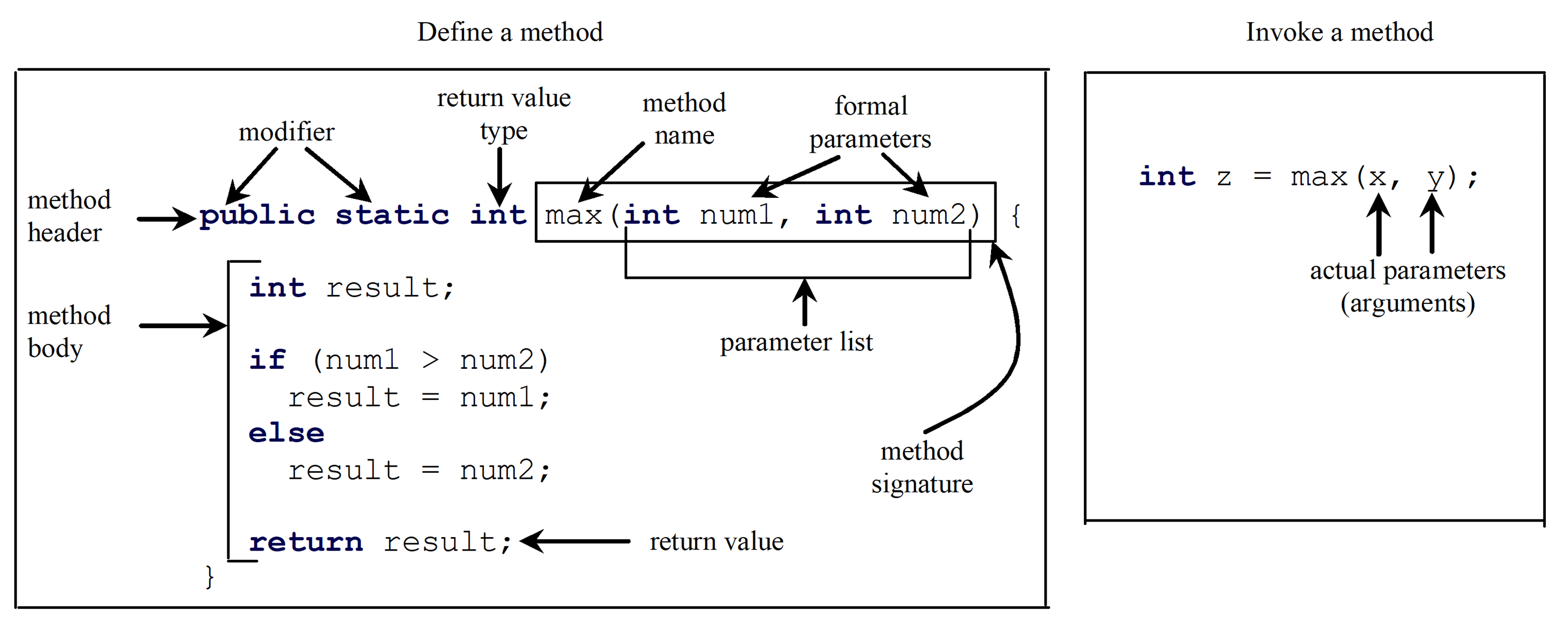
Defining Methods
A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation.
//Define method
public static int max(int num1,int num2){
int result;
if(num1>num2){
result=num1;
}else{
result=num2;
}
return result;
}
//Invoke method
int z=max(x,y); //x and y are the parameters or arguments
Defining Methods
- The variables defined in the method header are known as formal parameters.
- When a method is invoked, you pass a value to the parameter. This value is referred to as actual parameter or argument.
- The returnValueType is the data type of the value the method returns.
- If the method does not return a value, the returnValueType is the keyword void.
Method Signature
Code
- Method signature is the combination of the method name and the parameter list.
VISIBILITY
- VISIBILITY “modifiers” help reinforce encapsulation ideas by restricting a client’s ability to access an object.
- FINAL is used to create an unchangeable variable like a Constant.
- PRIVATE restricts access to an object to the members of the object’s class.
- PRIVATE METHODS are known as SUPPORT Methods.
- PUBLIC visibility allows the object to be referenced anywhere
- PUBLIC METHODS are known as SERVICE Methods
- PROTECTED- visibility by classes only in the same package
class Visibility {
private static String name="IS147";
public static String myName(String name){
return name;
}
static int myName(int myclass){
return myclass;
}
}
Passing Parameters
- Suppose you invoke the method using nPrintln(“Welcome to Java”, 5); What is the output?
- Suppose you invoke the method using nPrintln(“Computer Science”, 15); What is the output?
- Can you invoke the method using nPrintln(15,"Computer Science");
public static void nPrintln(String message, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.println(message);
}
nPrintln(“Welcome to Java”, 5);
nPrintln(“Computer Science”, 15);
nPrintln(15,"Computer Science");
void Method Example
This type of method does not return a value. The method performs some actions.
public class TestVoidMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("The grade is ");
printGrade(78.5);
System.out.print("The grade is ");
printGrade(59.5 );
}
public static void printGrade(double score) {
if (score >= 90.0) {
System.out.println('A');
}
else if (score >= 80.0) {
System.out.println('B');
}
else if (score >= 70.0) {
System.out.println('C');
}
else if (score >= 60.0) {
System.out.println('D');
}
else {
System.out.println('F');
}
}
}
Method Return value
Any method that is not declared void must contain a return statement.
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (items.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
boolean myvalue=isEmpty();
Pass By Value
Pass by Value
public class TestPassByValue {
/** Main method */
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and initialize variables
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
System.out.println("Before invoking the swap method, num1 is " +
num1 + " and num2 is " + num2);
// Invoke the swap method to attempt to swap two variables
swap(num1, num2);
System.out.println("After invoking the swap method, num1 is " +
num1 + " and num2 is " + num2);
}
/** Swap two variables */
public static void swap(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.println("\tInside the swap method");
System.out.println("\t\tBefore swapping, n1 is " + n1
+ " and n2 is " + n2);
// Swap n1 with n2
int temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;
System.out.println("\t\tAfter swapping, n1 is " + n1
+ " and n2 is " + n2);
}
}
Modularizing Code
- Methods can be used to reduce redundant coding and enable code reuse.
- Methods can also be used to modularize code and improve the quality of the program.
public class PrimeNumberMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("The first 50 prime numbers are \n");
printPrimeNumbers(50);
}
public static void printPrimeNumbers(int numberOfPrimes) {
final int NUMBER_OF_PRIMES_PER_LINE = 10; // Display 10 per line
int count = 0; // Count the number of prime numbers
int number = 2; // A number to be tested for primeness
// Repeatedly find prime numbers
while (count < numberOfPrimes) {
// Print the prime number and increase the count
if (isPrime(number)) {
count++; // Increase the count
if (count % NUMBER_OF_PRIMES_PER_LINE == 0) {
// Print the number and advance to the new line
System.out.printf("%-5d\n", number);
}
else
System.out.printf("%-5d", number);
}
// Check if the next number is prime
number++;
}
}
/** Check whether number is prime */
public static boolean isPrime(int number) {
for (int divisor = 2; divisor <= number / 2; divisor++) {
if (number % divisor == 0) { // If true, number is not prime
return false; // number is not a prime
}
}
return true; // number is prime
}
}
Overloading Methods
- Creating a different method with the same name in the same class, but with a different parameter list.
- The return type can be freely modified.
- The access modifier (public, private, and so on) can be freely modified.
- The method parameters must change: either the number or the type of parameters must be different in the two methods.
public class MethodOverload {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(write(12));
System.out.println(write("Twelve"));
System.out.println(write(4,16));
}
public static String write(int num){
return ("Int passed is " +num);
}
public static String write(String num){
return ("String passed is " +num);
}
public static String write(int num1,int num2){
return ("Sum Total is " +(num1+num2));
}
}
Method Overloading
Ambiguous Invocation
- Sometimes there may be two or more possible matches for an invocation of a method, but the compiler cannot determine the most specific match. This is referred to as ambiguous invocation. Ambiguous invocation is a compile error. Code
Ambiguous Invocation Example
public class AmbiguousOverloading {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(max(1, 2));
}
public static double max(int num1, double num2) {
if (num1 > num2)
return num1;
else
return num2;
}
public static double max(double num1, int num2) {
if (num1 > num2)
return num1;
else
return num2;
}
}
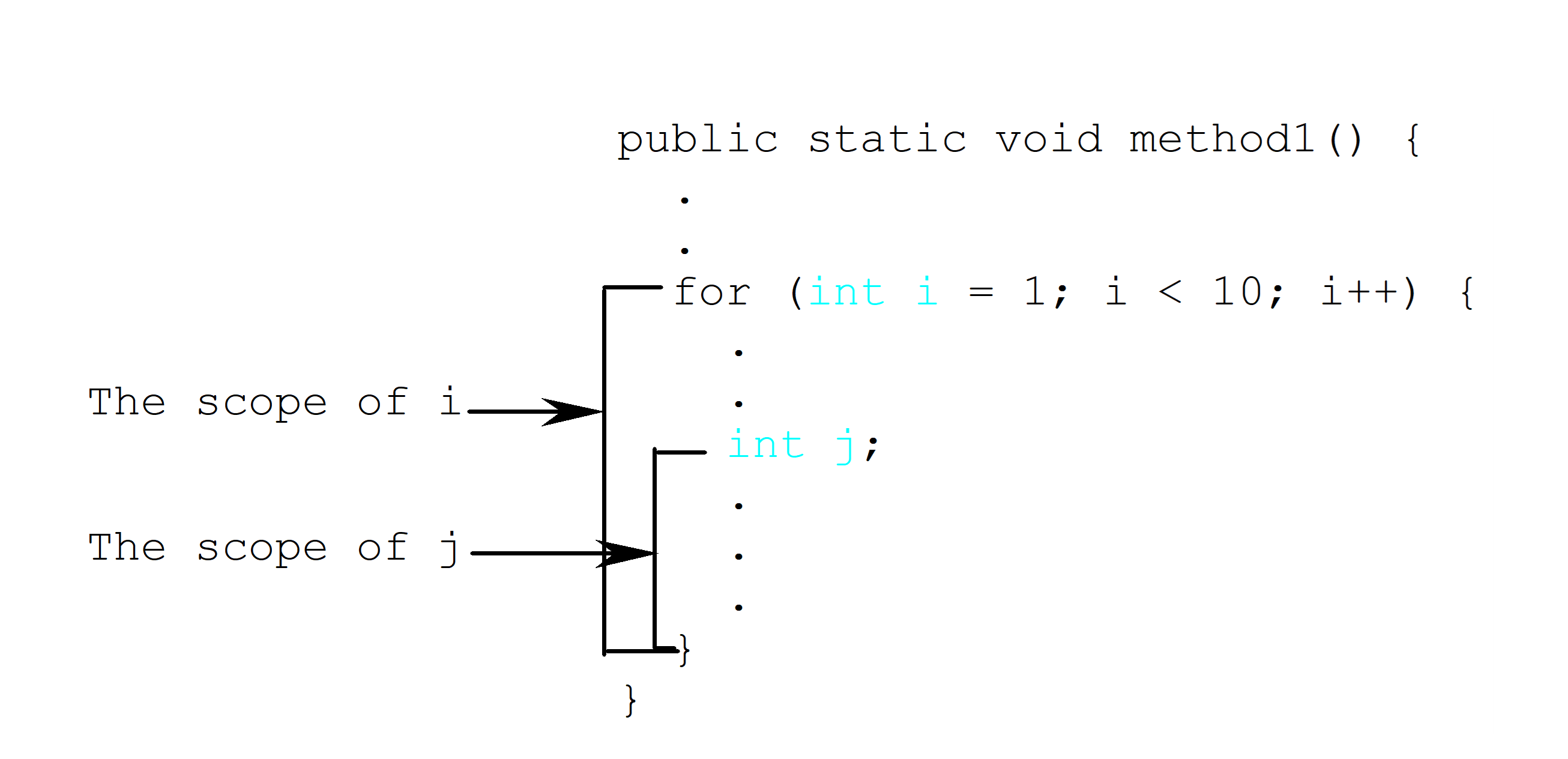
Scope of Local Variables
- A local variable: a variable defined inside a method.
- Scope: the part of the program where the variable can be referenced.
- The scope of a local variable starts from its declaration and continues to the end of the block that contains the variable. A local variable must be declared before it can be used.
- You can declare a local variable with the same name multiple times in different non-nesting blocks in a method, but you cannot declare a local variable twice in nested blocks.
- A variable declared in the initial action part of a for loop header has its scope in the entire loop. But a variable declared inside a for loop body has its scope limited in the loop body from its declaration and to the end of the block that contains the variable.
Scope of Local Variables Example

Scope
code
Scope Examples
// Fine with no errors
public static void correctMethod() {
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
// i is declared
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
x += i;
}
// i is declared again
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
y += i;
}
}
// With errors
public static void incorrectMethod() {
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
int x = 0;
x += i;
}
}
Method Abstraction
- You can think of the method body as a black box that contains the detailed implementation for the method.
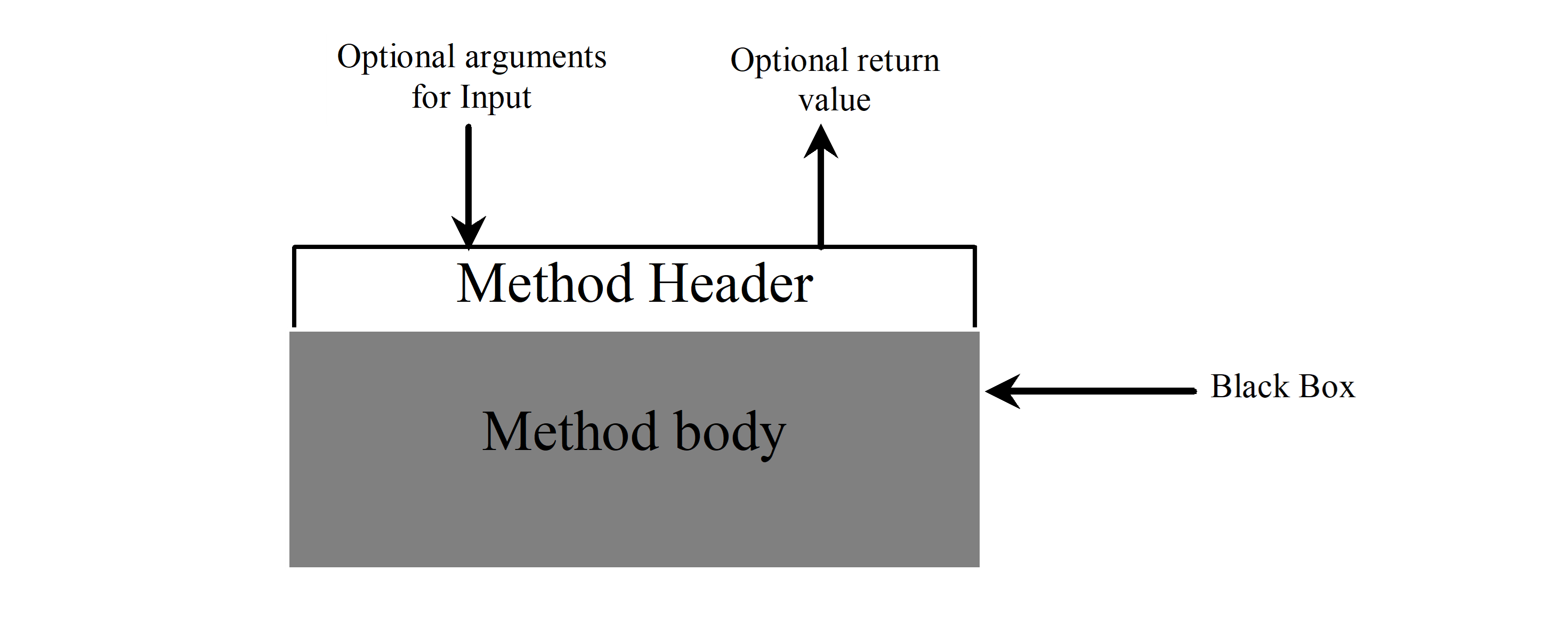
Benefits of Methods
- Write a method once and reuse it anywhere.
- Information hiding. Hide the implementation from the user.
- Reduce complexity
// RandomCharacter.java: Generate random characters
public class RandomCharacter {
/** Generate a random character between ch1 and ch2 */
public static char getRandomCharacter(char ch1, char ch2) {
return (char)(ch1 + Math.random() * (ch2 - ch1 + 1));
}
/** Generate a random lowercase letter */
public static char getRandomLowerCaseLetter() {
return getRandomCharacter('a', 'z');
}
/** Generate a random uppercase letter */
public static char getRandomUpperCaseLetter() {
return getRandomCharacter('A', 'Z');
}
/** Generate a random digit character */
public static char getRandomDigitCharacter() {
return getRandomCharacter('0', '9');
}
/** Generate a random character */
public static char getRandomCharacter() {
return getRandomCharacter('\u0000', '\uFFFF');
}
}
Stepwise Refinement (Optional)
The concept of method abstraction can be applied to the process of developing programs. When writing a large program, you can use the “divide and conquer” strategy, also known as stepwise refinement, to decompose it into subproblems. The subproblems can be further decomposed into smaller, more manageable problems.
Print Calendar Example
Method Refinement
@startwbs
!theme cyborg-outline
* printCalendar(main)
** readInput
*** printMonth
*** printMonthTitle
** printMonthBody
*** getMonthName
**** getStartDay
**** getTotalNumofDatys
*** getNumofDaysinMonth
*** idLeapYear
@endwbs
@startwbs
!theme cyborg-outline
* printCalendar(main)
** readInput
*** printMonth
*** printMonthTitle
** printMonthBody
*** getMonthName
**** getStartDay
**** getTotalNumofDatys
*** getNumofDaysinMonth
*** idLeapYear
@endwbs