Chapter 4

Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
Mathematical Functions
Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common mathematical functions.
The Math Class
Class methods
- Trigonometric Methods
- Exponent Methods
- Rounding Methods
- min, max, abs, and random Methods
Trigonometric Methods
Examples:
Math.sin(0) returns 0.0
Math.sin(Math.PI / 6) returns 0.5
Math.sin(Math.PI / 2) returns 1.0
Math.cos(0) returns 1.0
Math.cos(Math.PI / 6) returns 0.866
Math.cos(Math.PI / 2) returns 0
Exponent Methods
Rounding Methods
- double ceil(double x) x rounded up to its nearest integer. This integer is returned as a double value.
- double floor(double x) x is rounded down to its nearest integer. This integer is returned as a double value.
- double rint(double x) x is rounded to its nearest integer. If x is equally close to two integers, the even one is returned as a double.
- int round(float x) Return (int)Math.floor(x+0.5).
- long round(double x) Return (long)Math.floor(x+0.5).
Rounding Methods Examples
min, max, and abs
- max(a, b)and min(a, b) Returns the maximum or minimum of two parameters.
- abs(a) Returns the absolute value of the parameter.
- random() Returns a random double value in the range (0.0, 1.0).
The random method
- Generates a random double value greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0 (0 <= Math.random() < 1.0)
Returns a random integer between 0 and 9
(int)(Math.random()*10)
--------------------------------------------------
Returns a random integer between 50 and 99
50 + (int)(Math.random() * 50 )
--------------------------------------------------
a + Math.random() * b
Returns a random number between a and a+b, excluding a+b.
Math Examples
Character Data Type
Character may contain a single field whose type is char
The char data type is a primitive data type and is widely used for handling text and characters in Java programs.
char letter ='A' (ASCII)
char numChar ='4' (ASCII)
char letter='\u0041' (Unicode)
char numchar='\u0043' (Unicode)
Character Examples
public class CharInString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String message = "Hello, World!";
char firstChar = message.charAt(0); // Get the first character
char lastChar = message.charAt(message.length() - 1); // Get the last character
System.out.println("First Character: " + firstChar);
System.out.println("Last Character: " + lastChar);
}
}
ASCII Table
Character Data Types
Sample code on Github character code
Special String Characters
String txt="We are the so-called "Vikings" from the north";
| Special Character | Display |
|---|---|
| \' | Single quotation mark |
| \" | Double quotation mark |
| \\ | Backslash |
| \t | Tab |
| \r or \n | Carriage return |
Special String Characters

Comparing and Testing Characters
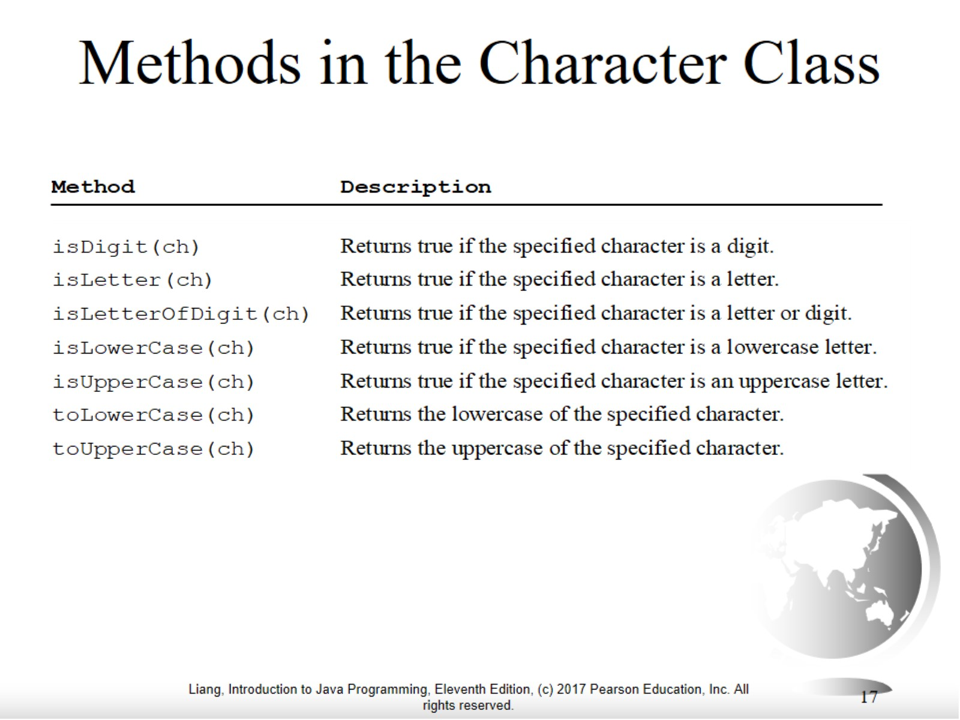
Character Method example
char ch='A';
System.out.println( Character.isDigit(ch));
System.out.println(Character.isAlphabetic(ch));
System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase(ch));
The String Type
In Java, the String type is used to represent a sequence of characters. It is one of the most commonly used data types for handling text and is part of the java.lang package. Strings in Java are immutable , meaning once a String object is created, its value cannot be changed. Instead, any operation that modifies a String creates a new String object.
What is String?
String is actually a predefined class in the Java library just like the System class and Scanner class.
Any Java class can be used as a reference type for a variable.
It is known as a reference type.
The String type is not a primitive type.


String Examples
Sample code on Github string code
String Immutability
Strings in Java are immutable. This means that once a String object is created, its value cannot be changed.
String str = "Hello";
str = str + " World!"; // Creates a new String object
System.out.println(str); // Output: Hello World!
In the above example, the original string "Hello" is not modified. Instead, a new string "Hello World!" is created
Immutable Example
How String store value?

String Equality?
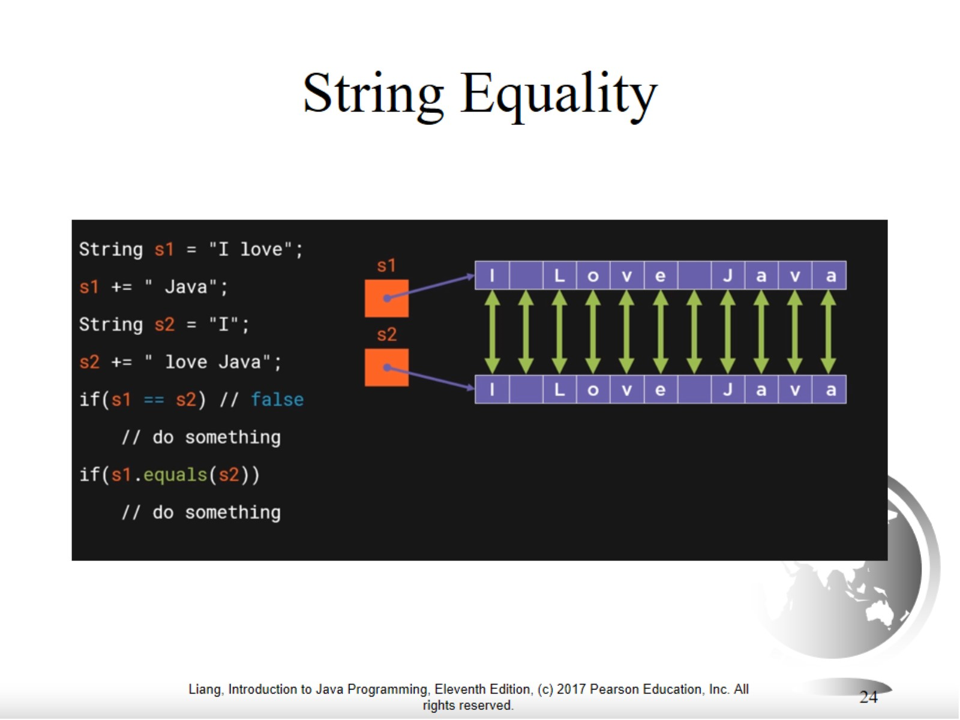
Interned String
String Interning in Java is a process where identical strings are searched in the string pool and if they are present, the same memory is shared with other strings having the same value.
The intern() method creates an exact copy of a String that is present in the heap memory and stores it in the String constant pool.
Note - intern() method is used to store the strings that are in the heap in the string constant pool if they are not already present.
Interned String

Interned String
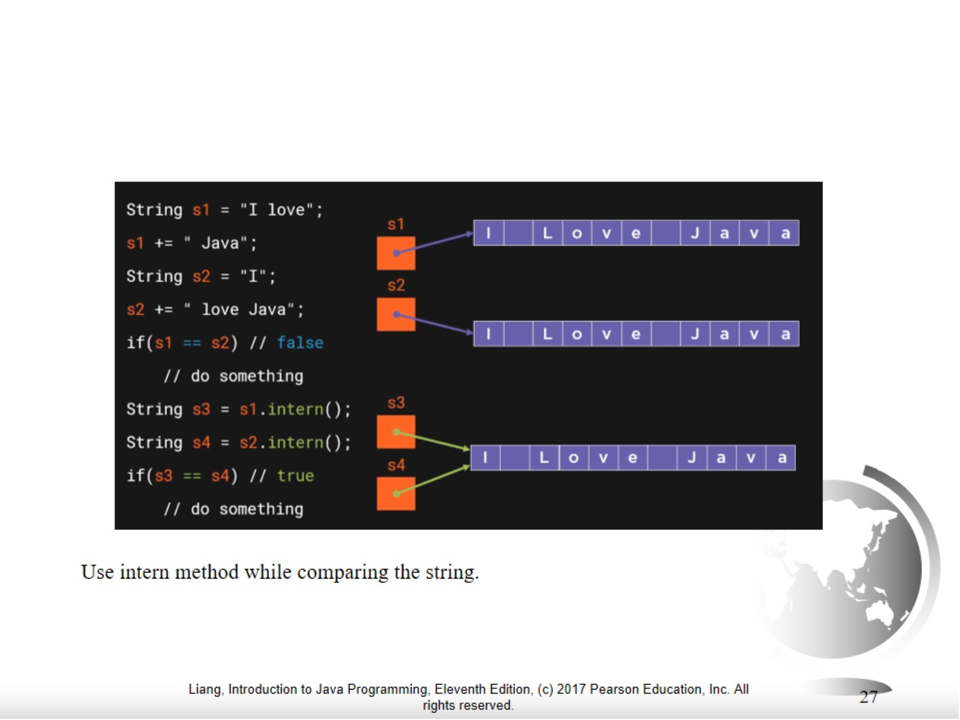
Interned Example
String Comparision
Best Pratices
- Use equals() not == to compare two strings
- == operator compares memory location
- While equals() method compare the content stored in two objects
- s1.equal(s2)

Converting Strings
System.out.println("welcome".toLowerCase());//return a new string welcome.
System.out.println("welcome".toUpperCase()) ;//return a new string WELCOME.
System.out.println(" Welcome ".trim()) ;//returns a new string , Welcome
String Concatenation
String s1= "IS147";
String s2="JAVA";
String s3=s1.concat(s2);
String s4=s1+s2;
//Three strings are concatenated
String message="Welcome" + " to" + "java";
//String chapter is concatenated with number 2
String s= "Chapter" + 2; // s becomes Chapter2
//String Supplement is concatenated with character b
String s5= "Supplement" + 'B'; //s1 becomes SupplementB
System.out.println(message);
System.out.println("Using concat " +s3);
System.out.printf("Using + symbol with number %s %n" ,s4);
System.out.printf("Using char + %s %n" ,s);
Immutable Example
- String objects are immutable. Immutable simply means unmodifiable or unchangeable.
- Once String object is created its data or state can't be changed but a new String object is created.
String Immutable
String Concatenation
String s3=s1.concat(s2); or String s3=s1+s2;
//Three strings are concatenated
String message="Welcome" + " to" + "java";
//String chapter is concatenated with number 2
String s "Chapter" + 2; // s becomes Chapter2
//String Supplement is concatenated with character b
String s1= "Supplement" + 'B'; //s1 becomes SupplementB

THE END
Questions
Group Project
- Lab 3