Java Basics

What is a program?
📚 Simple Explanation
- Computer programs are instructions to the computer
- You tell a computer what to do: Exactly what to do. Computers do not understand human languages, so you need to use a clear set of instructions to communicate your intent.
- It’s not unlike other specific instructions we need to follow.
Why Java?
- It’s been around for a while - developed by Sun Microsystems, now owned by Oracle
- A general-purpose object-oriented language Based on C/C++
- Designed for easy web/internet application development
- Widespread use/acceptance
- Simple, object oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architecture neutral, portable, high performance, multithreaded, and dynamic.
- Java Runs on Servers, PCs and laptops, Mobile and other devices
How do we use Java
- IDE
- Java Lang spec
- API
Anatomy of a Java Program
- Class name
- Main method
- Statements
- Statement terminator
- Reserved words
- Comments
- Blocks
Install Intellij
Programming Languages
hyperpolyglot.org/cppClass Name
- Every Java program must have at least one class
- Each class has a name
- By convention, class names start with an uppercase letter. In this example, the class name is Welcome.
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Main Method
- Line 3 defines the main method. In order to run a class, the class must contain a method named main.
- The program is executed from the main method.
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Statement
- A statement represents an action or a sequence of actions.
- The statement System.out.println("Welcome to Java!") in the program below is a statement to display the greeting "Welcome to Java!“.
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Statement Terminator
- Every statement in Java ends with a semicolon (;).
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Reserved words
- Reserved words or keywords are words that have a specific meaning to the compiler and cannot be used for other purposes in the program.
- For example, when the compiler sees the word class, it understands that the word after class is the name for the class.
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Blocks
- A pair of braces in a program forms a block that groups components of a program.
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome { //Class block
public static void main(String[] args) { // Method block
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Special Symbols
| Character | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {} | Opening and closing braces | Denotes a block to enclose statements. |
| () | Opening and closing parenthesis | Used with methods. |
| [] | Opening and closing brackets | Denotes an array. |
| // | Double slashes | Precedes a comment line |
| "" | Opening and closing quotation marks | Enclosing a string (i.e., sequence of characters) |
| ; | Semicolon | Marks the end of a statement |
| /* ... */ | Multiline comment | Comment multiple lines |
{ Opening and closing braces }
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome { //opening curly
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}//closing curly
(Opening and closing parenthesis)
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) // parenthesis{
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Semicolon ;
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!"); //semicolon
}
}
Double slashes //
// This program prints Welcome to Java! //This is single line comment
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
"Opening and closing quotation marks"
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!"); //String values wrapped in a comment
}
}
"/* Multi line comment */"
/* This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
*/ //Multi line comment
Programming Style and Documentation
- Naming Conventions
- Class names:
- Capitalize the first letter of each word in the name. For example, the class name ComputeExpression
- Indentation :tab( or two spaces)
- Spacing: Use blank line to separate segments of the code.
public class Welcome //classname start with uppercase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
public class Welcome //classname start with uppercase
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Interpreting/Compiling Source Code
- A program written in a high-level language is called a source program or source code
- Because a computer cannot understand a source program, a source program must be translated into machine code for execution
- The translation can be done using another programming tool called an interpreter or a compiler.
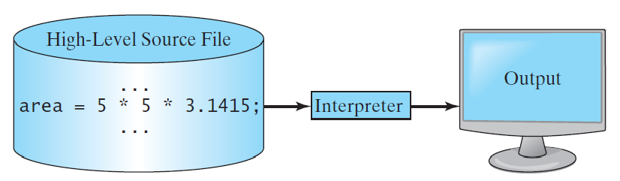
Interpreting Source Code
- An interpreter reads one statement from the source code, translates it to the machine code or virtual machine code, and then executes it right away
- Note that a statement from the source code may be translated into several machine instructions.
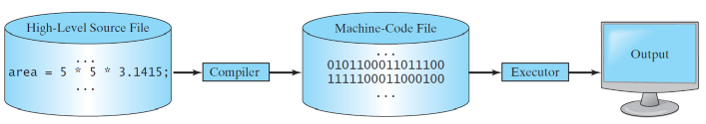
Compiling Source Code
- A compiler translates the entire source code into a machine-code file, and the machine-code file is then executed, as shown in the following figure.
- Java source code is converted to Byte code

Compile Java Code
- Javac filename e.g javac myfile.java
- Java myfile
- javac FirstJavaApp.java
- Java FirstJavaApp anything something other words

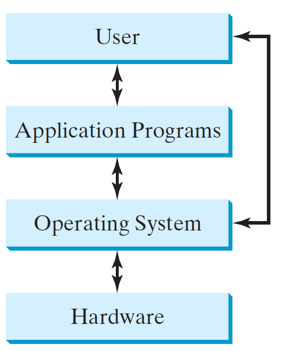
Operating Systems
- The operating system (OS) is a program that manages and controls a computer’s activities.
- Popular OS Windows,MAC OS and Linux
- such as a Web browser or a word processor, cannot run unless an operating system is installed and running on the computer
Platform Independence
- Write code once
- Compiled code can run on any platform that has JRE
- JRE is platform dependent
Programming Errors
- Syntax Errors => Detected by the compiler
- Runtime Errors => Causes the program to abort
- Logic Errors => Produces incorrect result
Syntax Errors
Runtime Errors
Logical Errors
TAKE-AWAYS
- With computers, precise instructions are extremely important
- If you have missing, incorrect, or misspelled words/punctuation, it will reject your instructions